Quality Data Matters: Essential Factors for Successful Aerial Photogrammetry
In aerial photogrammetry, the quality of your data depends on not only your equipment but also on you. As a practitioner in this dynamic field, your expertise, attention to detail, and adherence to best practices are paramount for achieving accurate and reliable results. From meticulously planning flight missions to fine-tuning camera settings and conducting thorough post-processing and georeferencing, every step of the workflow plays a crucial role in shaping the outcome of your dataset. In this article, we’ll delve into some essential factors that contribute to data quality and explore actionable strategies to ensure success in your endeavors.
Flight Planning & Execution
Effective flight planning is the cornerstone of successful photogrammetry missions. Factors such as altitude, overlap and camera settings must be carefully considered to optimize data capture and ensure adequate coverage of the target area.
Ensuring that you have quality overlap is one of the most important factors in flying your mission. Good overlap between images ensures that there are enough common points for stitching the images together accurately, resulting in a cohesive and precise dataset. Conversely, poor overlap can lead to gaps in data, increased errors and a reduction in the overall quality of the final output.
For a more detailed discussion on imagery overlap, visit our blog post: Importance of Imagery Overlap.
Weather & Lighting Conditions
Weather can significantly impact the quality of your data. For instance, flying in windy conditions can lead to unstable flight paths, resulting in blurry images. Similarly, flying under overcast skies can diffuse light evenly, reducing shadows but can potentially end up affecting the contrast needed for accurate data capture. Consideration of weather conditions is crucial for safe and successful flights.
Optimal lighting conditions, such as clear skies and consistent lighting angles can enhance image clarity and minimize shadows, thereby improving your data quality.

Nadir view of well lit construction site with minimal shadows and high, full sun.

View of low, indirect lighting with long shadows dataset which may impact residual error and image connectivity.

Nadir photo of freighter stern deck taken at dusk, resulting in a blurry photo due to the drone camera having a rolling shutter, low light and too fast of flight speed.
A good figure to use when trying to compensate for motion blur is given from the ASPRS Positional Accuracy Standards for Digital Geospatial Data: Addendum VI. Ultimately, it is the pilot’s responsibility to compensate for such motion blur, as the gimbal, camera, and softwares can only do so much to stabilize and capture an image with sharp and clear resolution.
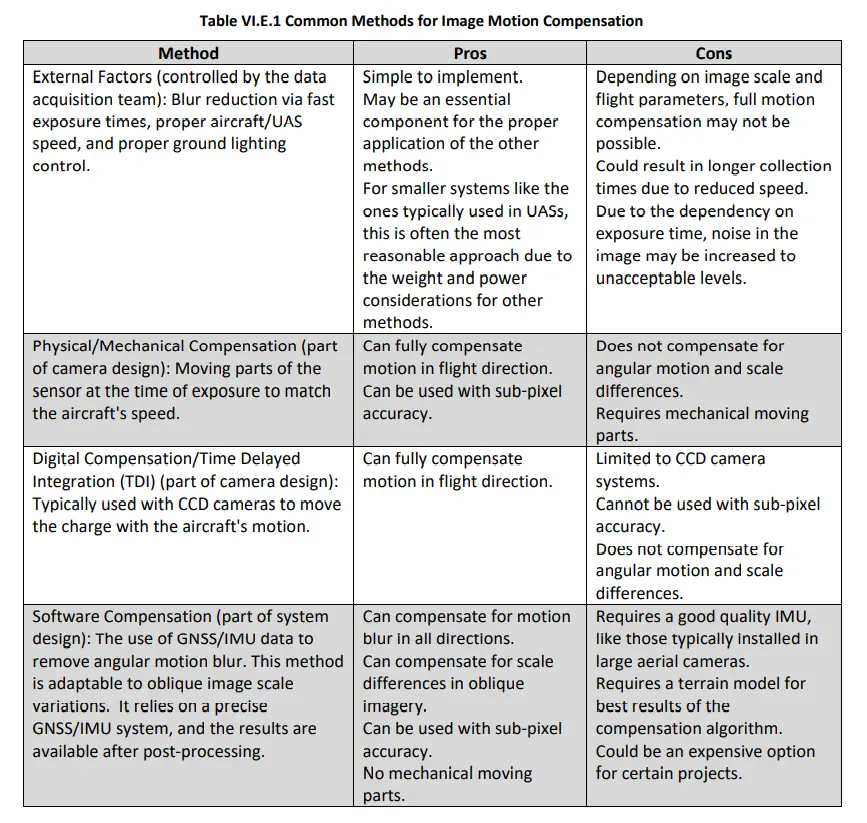
Camera Settings
From adjusting aperture and shutter speed to fine-tuning ISO sensitivity or using ND filters, every parameter influences the quality and accuracy of your captured images. Ensuring proper synchronization between camera settings and flight conditions is essential for achieving sharp, well-exposed images with minimal distortion. To mitigate the distortion of images when using a rolling shutter (like many entry level drones), be sure to use a drone that has a mechanical shutter for best results. However, mechanical shutters also have their downsides, as noted in the figure above. Poor image quality can lead to significant errors and inaccuracies in the final 3D models and maps.
Flight Path Planning
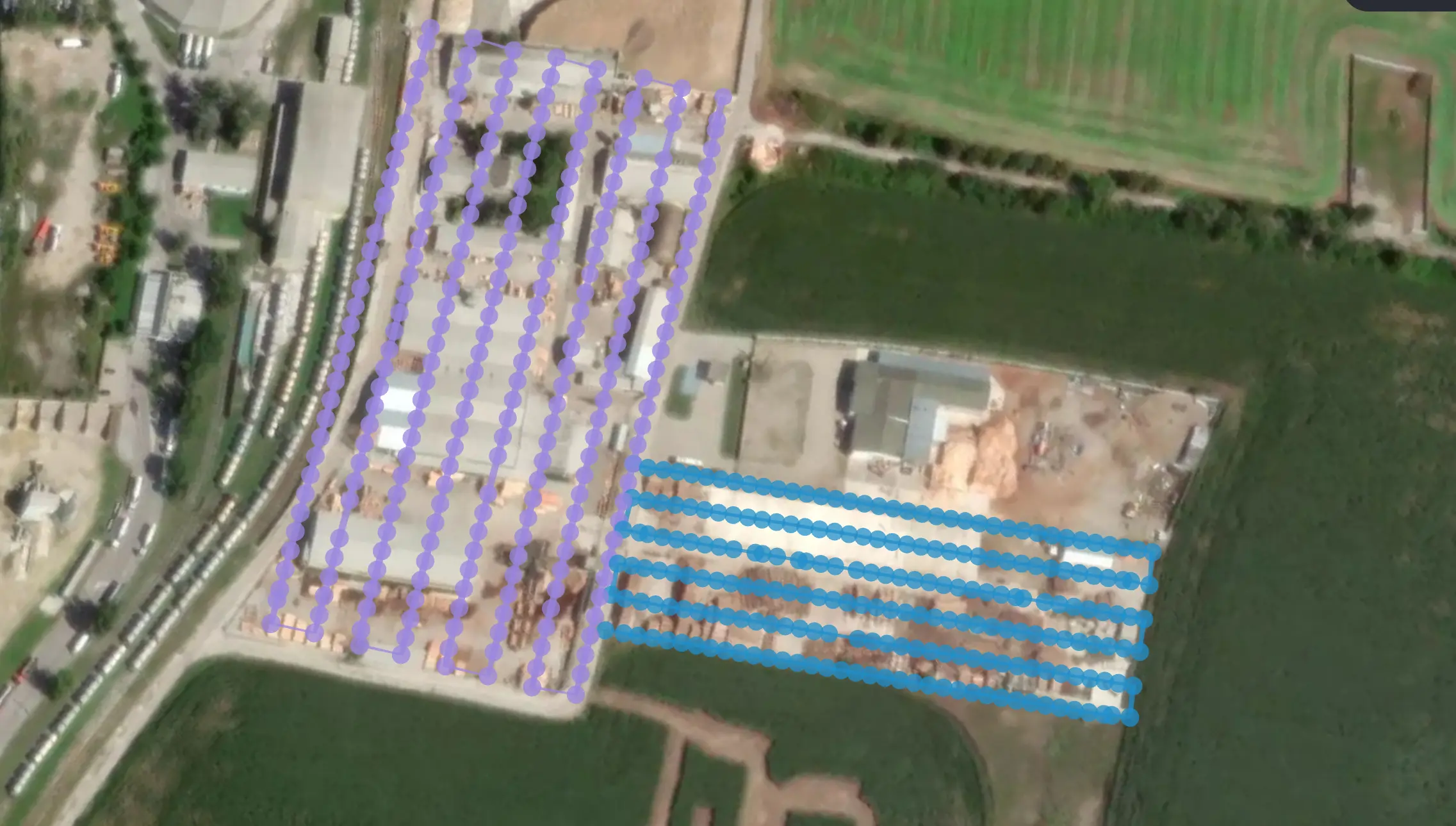

Aerial flight paths and images taken over project site
Utilizing advanced flight planning software or tools can aid in generating optimal routes tailored to the specific requirements of your project. By positioning ground control points or using RTK/PPK equipped drones, and adjusting flight parameters, such as speed and altitude, you can enhance coverage, reduce flight time and ultimately optimize data acquisition.
Micro Drones
If you are flying a micro drone (DJI Mini 3 Pro or earlier) manually that is not able to fly autonomously to capture your site, be cognisant of several critical factors to ensure the quality of your data:
- Consistency in Flight Path: Maintain a consistent and stable flight path to ensure uniform data capture. Sudden changes in direction or altitude can lead to gaps or overlaps in your data.
- Manual Overlap Control: Pay close attention to the overlap between images. Aim for a minimum of 60-70% forward and side overlap to ensure comprehensive coverage and accurate stitching of images.
- Speed Management: Fly at a steady and controlled speed to prevent motion blur and to capture clear, sharp images. Adjust your speed based on the complexity of the terrain and the desired resolution.
- Altitude Awareness: Maintain a constant altitude during the flight to ensure consistent image resolution and scale. Use altitude markers or visual references to help keep your drone at the correct height.
- Environmental Awareness: Be aware of environmental factors such as wind, obstacles, and lighting conditions that can affect your flight. Plan your flight path to avoid areas with potential hazards and to take advantage of optimal lighting conditions.
Battery Management
When out in the field, effective battery management is also crucial for uninterrupted flight operations and ensuring data integrity. Prioritize monitoring battery levels throughout the flight and implement protocols for safe return-to-home procedures when batteries reach predefined thresholds. Additionally, consider factors such as temperature and flight duration when planning battery usage to mitigate unexpected power depletion mid-flight.
Conclusion
The quality of your data is influenced by numerous factors that extend beyond just your equipment. Your expertise, meticulous planning and adherence to best practices play a crucial role in capturing accurate and reliable data. By focusing on the discussed factors and employing actionable strategies, you can significantly enhance the quality of your aerial photogrammetry projects.
Please see our article about the most recent updates to the American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing’s best practices guidelines to learn how to best practice your data collection and post-processing here.
To view our playlists including tutorial videos, project featurettes and new features here.